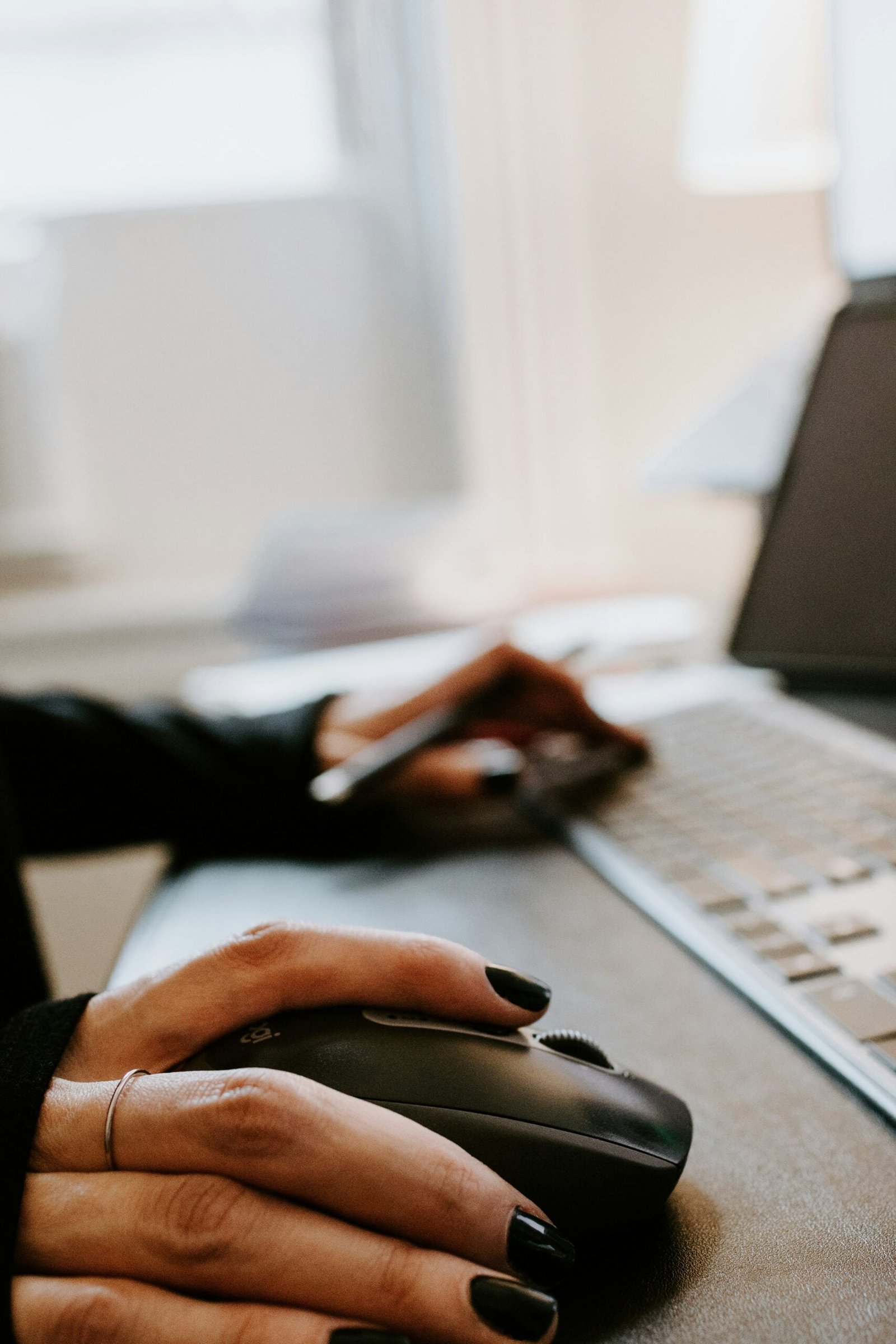
Unlike an optical mouse, which uses an LED light to track movement, a laser sensors mouse uses a laser beam to detect changes in position. This laser beam emits a concentrated and highly focused light that is reflected off the surface beneath the mouse. The sensor in the mouse then analyzes the reflected light to determine the mouse’s movement.
One of the main advantages of a laser sensors mouse is its increased sensitivity and precision. The laser beam allows for more accurate tracking, even on uneven or glossy surfaces that may pose challenges for an optical mouse. This makes it an ideal choice for gamers, graphic designers, and anyone who requires precise cursor control.
In addition to its improved accuracy, a laser sensors mouse also offers a higher resolution. This means that it can detect smaller movements and provide a smoother cursor movement on the screen. The higher resolution is especially beneficial for tasks that require fine detail, such as photo editing or CAD design.
Another key feature of a laser sensors mouse is its ability to work on a wider range of surfaces. While an optical mouse may struggle on certain materials like glass or shiny surfaces, a laser sensors mouse can track movement effortlessly on these surfaces. This versatility makes it a convenient choice for users who often work in different environments or need to use their mouse on various surfaces.
Furthermore, a laser sensors mouse typically has a higher polling rate compared to an optical mouse. The polling rate refers to how often the mouse reports its position to the computer. A higher polling rate means that the mouse updates its position more frequently, resulting in a more responsive and smoother cursor movement.
Overall, a laser sensors mouse offers superior performance and accuracy compared to an optical mouse. Its advanced technology and precision tracking make it an excellent choice for professionals who require precise cursor control and smooth movement. Whether you are a gamer, a graphic designer, or simply someone who values accuracy, a laser sensors mouse is a worthwhile investment.
The sensor in a laser mouse is a crucial component that enables accurate tracking of movement. It is designed to detect the reflected laser light and convert it into movement data that can be interpreted by the computer. The sensor consists of a photodiode, which is a semiconductor device that converts light into an electrical current. When the laser beam hits the surface, it reflects back and enters the sensor through a lens.
Inside the sensor, the reflected light is split into multiple beams using a beam splitter. Each beam is then directed onto a separate photodiode. The photodiodes measure the intensity of the light they receive and convert it into an electrical signal. The signals from the photodiodes are then processed by a microcontroller, which calculates the changes in position and distance based on the differences in intensity between the beams.
The microcontroller uses complex algorithms to analyze the data and determine the direction and speed of the mouse movement. It takes into account factors such as the surface texture, the angle of the laser beam, and the distance between the mouse and the surface. By continuously updating the position data, the microcontroller can accurately track the mouse’s movement in real-time.
In addition to its precision, a laser mouse offers other advantages over optical mice. The laser beam is more focused and concentrated, allowing it to track movement on a wider range of surfaces, including glass and glossy materials. This versatility makes laser mice suitable for various environments, such as offices, gaming setups, and even outdoor use.
Furthermore, laser mice often have higher sensitivity settings, which means they can track even the smallest movements with great precision. This makes them particularly popular among gamers and graphic designers who require precise control over their cursor movements.
How Does a Laser Mouse Work?
A laser mouse works by combining several components to accurately track movement. These components include:
- Laser Diode: The laser diode emits the laser beam that is used to track movement. It is usually located at the bottom of the mouse.
- Sensor: The sensor captures the reflected laser light and converts it into digital signals. This allows the mouse to track the movement of the surface it is placed on.
- Processor: The processor in the mouse analyzes the signals from the sensor and calculates the mouse’s position and movement.
- USB Connection: The mouse is connected to the computer via a USB cable or wireless connection. This allows the processed data to be transmitted to the computer, enabling the cursor to move on the screen.
When you move the laser mouse across a surface, the laser diode emits a focused beam of light onto the surface. The sensor then captures the light that is reflected back from the surface. This reflected light contains information about the surface’s texture and color, which the sensor uses to determine the mouse’s movement.
The captured light is converted into digital signals by the sensor, which are then sent to the processor. The processor analyzes these signals and calculates the mouse’s position and movement based on the changes in the reflected light. It also takes into account factors such as the speed and direction of the mouse’s movement.
Once the processor has calculated the mouse’s position and movement, it sends this information to the computer via the USB connection. The computer uses this data to move the cursor on the screen accordingly. The cursor’s movement is smooth and responsive, thanks to the accurate tracking provided by the laser mouse.
In addition to accurate tracking, laser mice also offer other advantages over traditional optical mice. The laser diode used in laser mice emits a more focused and precise beam of light compared to the LED used in optical mice. This allows laser mice to track movement on a wider range of surfaces, including glossy or uneven ones.
Furthermore, laser mice tend to have higher DPI (dots per inch) sensitivity compared to optical mice. This means that laser mice can detect smaller movements and provide more precise control over the cursor’s movement on the screen. This can be particularly beneficial for tasks that require fine cursor control, such as graphic design or gaming.
Overall, the combination of the laser diode, sensor, processor, and USB connection allows a laser mouse to accurately track movement and provide a smooth and responsive user experience. Whether you’re navigating through documents, editing photos, or playing video games, a laser mouse offers precise control and enhanced performance.
Mouse Sensor Laser vs. Optical
When comparing a mouse sensor laser to an optical mouse, there are a few key differences to consider:
Precision and Accuracy: Laser mice generally offer higher precision and accuracy compared to optical mice. The laser technology allows for more sensitive tracking, making it ideal for tasks that require precise cursor control, such as graphic design or gaming. The laser sensor can detect even the smallest movements, resulting in smoother and more precise tracking. This can be particularly advantageous in situations where accuracy is crucial, such as when editing intricate details in an image or navigating through complex gaming environments.
Surface Compatibility: Laser mice can track movement on a wider range of surfaces compared to optical mice. The laser beam used in a laser mouse can penetrate various surfaces, including glass and glossy surfaces, whereas optical mice may struggle to track on these surfaces. This versatility allows laser mice to be used on different types of desks, mouse pads, and even unconventional surfaces, providing users with greater flexibility in their choice of working environment.
Sensitivity: Laser mice tend to be more sensitive than optical mice. They can track at higher DPI (dots per inch) settings, allowing for faster and more responsive cursor movement. This can be beneficial for users who prefer a higher sensitivity for tasks that require quick cursor movements, such as gaming or fast-paced video editing. With a laser mouse, users can easily adjust the DPI settings to suit their preferences and achieve the desired level of sensitivity.
Power Consumption: Laser mice typically consume more power compared to optical mice. The laser diode requires more energy to operate, which can result in shorter battery life for wireless laser mice. However, this may not be a significant concern for users who primarily use their mouse with a wired connection. Additionally, advancements in technology have led to more energy-efficient laser mice, reducing the impact on battery life. Some laser mice also come with features like automatic sleep mode or power-saving options to help conserve energy when not in use.
Ultimately, the choice between a mouse sensor laser and an optical mouse depends on the user’s specific needs and preferences. Laser mice are often favored by professionals who require precise cursor control, while optical mice may be more suitable for everyday use. It’s important to consider factors such as the intended usage, the type of surfaces the mouse will be used on, and the desired level of sensitivity before making a decision. By understanding the differences between these two types of mice, users can make an informed choice that best suits their requirements.
Is a Laser Mouse Dangerous?
When used as intended, a laser mouse is not considered dangerous. The laser beam used in a laser mouse is low-powered and is designed to be safe for human use. It is important to note that the laser beam emitted by a laser mouse is not the same as the high-powered lasers used in industrial or medical applications.
However, it is always recommended to avoid directly staring into the laser beam or pointing it at someone’s eyes. While the chances of harm are minimal, it is best to exercise caution and use the laser mouse in a responsible manner.
Additionally, it is worth noting that laser mice are designed to emit the laser beam downwards onto the surface they are placed on. This means that the laser beam is not typically exposed to direct contact with the user’s skin.
In summary, a laser mouse is generally safe to use and poses no significant risks when used properly. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions and exercise caution to ensure a safe and enjoyable user experience.
Furthermore, laser mice have become increasingly popular due to their precision and accuracy. The laser technology used in these mice allows for smoother and more responsive tracking, making them ideal for tasks that require fine control, such as graphic design or gaming.
Moreover, laser mice often come with customizable features that allow users to adjust the sensitivity of the mouse to their liking. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals who require precise movements, such as professional photographers or video editors.
Additionally, laser mice are compatible with a wide range of surfaces, including glass and glossy surfaces, which can be challenging for traditional optical mice. This versatility makes laser mice a practical choice for users who work in various environments.
Another advantage of laser mice is their wireless capabilities. Many laser mice are equipped with Bluetooth or RF technology, allowing users to connect them to their computers without the hassle of cords or cables. This wireless freedom provides convenience and flexibility, especially for those who prefer a clutter-free workspace.
In conclusion, a laser mouse is not dangerous when used correctly. It offers numerous benefits, including precision, customization, compatibility with different surfaces, and wireless capabilities. By following the manufacturer’s guidelines and exercising caution, users can enjoy a safe and efficient computing experience with a laser mouse.