Keyboard layouts, such as QWERTY, Dvorak, and Colemak, vary in design and layout to optimize typing efficiency. Each layout has unique characteristics that impact typing speed and comfort, catering to different user preferences and needs.
Understanding the differences between these layouts can help individuals choose the one that best suits their typing style and enhances their overall typing experience. When comparing QWERTY, Dvorak, and Colemak keyboards, it’s important to consider factors such as key placement, finger movement, and ergonomics.
By delving into the specifics of each layout, users can make an informed decision on which one aligns best with their typing habits and requirements. Let’s explore the distinctive features and benefits of these keyboard layouts to navigate the diverse options available and select the most suitable one for enhanced typing proficiency.
History Of Keyboard Layouts
Understanding the history of keyboard layouts provides valuable insight into the development and evolution of the devices we use daily. Three prominent keyboard layouts, Qwerty, Dvorak, and Colemak, have distinct origins and have contributed to the diversity of choices available to users today. Exploring the origins of these keyboard layouts sheds light on the motivations behind their creation and the impact they have had on modern typing practices.
Qwerty Layout Origins
The Qwerty keyboard layout, named after the arrangement of its first six letters, was patented by Christopher Sholes in 1878 for the Sholes and Glidden typewriter. Designed to prevent jamming on early typewriters, the layout’s arrangement of letters aimed to separate commonly used pairs of letters to increase typing efficiency. Despite the emergence of several alternative layouts over the years, the Qwerty layout remains the dominant standard across the majority of keyboards.
Dvorak Layout Origins
The Dvorak Simplified Keyboard, developed by Dr. August Dvorak and his brother-in-law Dr. William Dealey in the 1930s, aimed to create a more efficient and ergonomic layout. Its design prioritizes vowel and consonant alternation, placing the most frequently typed keys in the home row for improved typing speed and comfort. Although the Dvorak layout has not achieved widespread adoption, it continues to be favored by enthusiasts who appreciate its purported ergonomic benefits.
Colemak Layout Origins
The Colemak keyboard layout, introduced by Shai Coleman in 2006, sought to optimize typing efficiency and comfort while maintaining compatibility with the Qwerty layout. Colemak’s design focuses on minimizing finger movement and maximizing the utilization of the home row. This approach aims to strike a balance between improved ergonomics and familiarity, appealing to users seeking an alternative layout that remains compatible with the existing Qwerty standard.
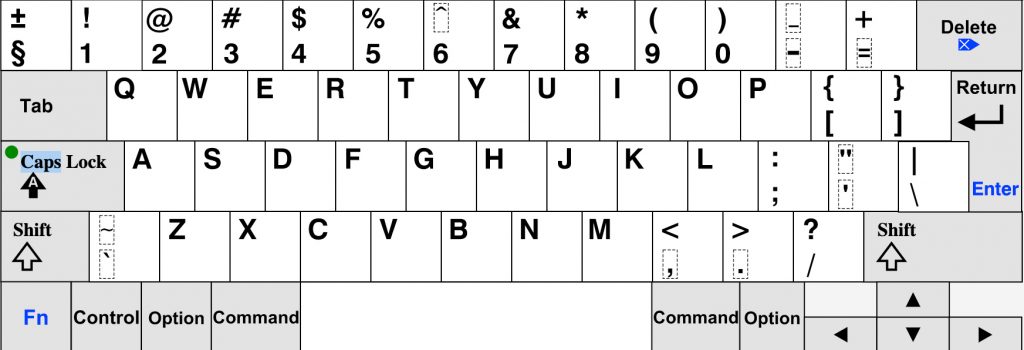
Qwerty Keyboard Layout
The Qwerty keyboard layout is the most commonly used keyboard layout in the world. Its name comes from the first six letters on the top row of keys. Designed in the 19th century by Christopher Sholes, the Qwerty keyboard layout was developed for mechanical typewriters and has since become the standard for computer keyboards. In this section, we will explore the layout design and characteristics of the Qwerty keyboard, as well as its advantages and disadvantages.
Layout Design And Characteristics
The Qwerty keyboard layout is a traditional layout that arranges the keys in a specific order. Each row of keys is offset from the row above it, creating a staggered effect. This layout is designed to maximize typing efficiency and reduce the likelihood of key jams on mechanical typewriters. The arrangement of the keys is based on the frequency of use of certain letters and the position of the fingers on the typewriter.
The Qwerty keyboard layout follows a specific pattern, with the most frequently used keys placed in easily accessible positions. The left hand is responsible for typing the keys on the left side of the keyboard, while the right hand types the keys on the right side. The center column of keys is shared by both hands, allowing for balanced typing between the two hands.
The Qwerty layout also includes additional keys, such as the Shift, Caps Lock, and Enter keys, as well as various function keys and punctuation marks. These keys are strategically placed to provide easy access while typing.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Although the Qwerty keyboard layout has been widely adopted and is familiar to most users, it does have both advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Easy to learn and widely used: The Qwerty layout is the standard keyboard layout and is taught in schools and used in most workplaces.
- Familiarity and muscle memory: Most people are accustomed to the Qwerty layout and have developed muscle memory, making typing faster and more efficient.
- Compatibility: The Qwerty layout is compatible with various operating systems and devices, making it versatile and accessible.
- Extensive resources and support: Due to its popularity, there are numerous resources, tutorials, and software designed specifically for Qwerty users.
Disadvantages:
- Typing inefficiency: The Qwerty layout was designed to prevent jams in mechanical typewriters, not for optimal finger placement. This can lead to inefficient finger movements and increased typing effort.
- Increased risk of repetitive strain injuries: The placement of keys on the Qwerty layout can lead to repetitive strain injuries, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, due to excessive finger stretching and awkward hand positions.
- Lower typing speed: Some alternative keyboard layouts claim to be more efficient and can potentially increase typing speed and accuracy compared to Qwerty.
Despite its disadvantages, the Qwerty keyboard layout remains the dominant layout in use today. However, alternative keyboard layouts, such as Dvorak and Colemak, have gained popularity among users seeking increased typing efficiency and ergonomics. In the following sections, we will explore these alternative layouts and compare them to the Qwerty layout.
Dvorak Keyboard Layout
The Dvorak keyboard layout is a potential alternative to QWERTY and Colemak layouts, designed to increase typing speed and comfort by placing the most commonly used keys within easy reach. Its ergonomic design offers a more efficient and intuitive typing experience.
Layout Design And Characteristics
The Dvorak keyboard layout, created by Dr. August Dvorak, is designed for improved typing efficiency.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages:
- Faster typing speeds.
- Reduced finger movement.
- Improved ergonomics.
- Increased comfort during long typing sessions.
Disadvantages:
- The need for users to retrain themselves.
- Compatibility issues with some operating systems.
- Limited availability on standard keyboards.
Credit: www.daskeyboard.com
Colemak Keyboard Layout
Colemak keyboard layout is an ergonomic alternative to QWERTY and Dvorak, designed for efficient and comfortable typing. It minimizes finger movement and strain, enhancing productivity and comfort for users. The layout is gaining popularity among those seeking a more optimized and ergonomic typing experience.
Colemak Keyboard Layout is designed to improve typing efficiency and reduce strain on fingers compared to Qwerty.
Layout Design And Characteristics
Colemak Layout optimizes key placement for improved ergonomics and comfort.
It places frequently used keys in easy-to-reach positions for faster typing speed.
The design focuses on minimizing finger movement to reduce fatigue during long typing sessions.
Colemak Layout retains some familiarity with Qwerty, making it easier to transition for most users.
Advantages And Disadvantages
Advantages:
– Colemak Layout increases typing speed by placing commonly used keys closer together.
– Users report fewer errors and less finger strain when using Colemak.
– Transitioning to Colemak may enhance overall typing comfort and efficiency.
Disadvantages:
– Learning a new keyboard layout like Colemak can be challenging initially.
– Compatibility issues may arise when using Colemak on different devices.
– Some shortcuts and hotkeys may need adjustment when using Colemak.
In conclusion, understanding the Colemak Keyboard Layout offers insight into optimizing typing comfort and efficiency.
Ergonomics And Efficiency
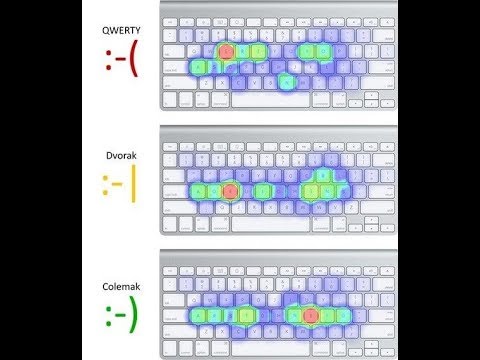
When it comes to keyboard layouts, two primary factors come into play: ergonomics and efficiency. Understanding the impact of different keyboard layouts on these factors can help you make an informed decision about which layout is best for you. In this post, we will delve into the comparison of typing efficiency and the impact on hand and finger movements for the three popular keyboard layouts: Qwerty, Dvorak, and Colemak.
Comparison Of Typing Efficiency
Typing efficiency is a crucial consideration when choosing a keyboard layout. It refers to the speed and accuracy at which you can type. Let’s compare the typing efficiency of the Qwerty, Dvorak, and Colemak layouts:
| Keyboard Layout | Typing Efficiency |
|---|---|
| Qwerty | Standard and widely used layout |
| Dvorak | Designed for increased typing efficiency |
| Colemak | Optimized for typing efficiency and minimal finger movement |
Qwerty: Qwerty is the traditional keyboard layout that most people are familiar with. While it has its advantages, such as easy learning curve and compatibility with various devices, it is not specifically designed for optimized typing efficiency.
Dvorak: Dvorak is an alternative keyboard layout that rearranges the keys for increased typing efficiency. It places commonly used keys on the home row, reducing the need to stretch your fingers. This layout aims to minimize finger movement and improve overall typing speed.
Colemak: Colemak is another modern alternative to Qwerty, focusing on typing efficiency and minimal finger movement. Like Dvorak, it rearranges the keys to optimize typing flow. Colemak aims to strike a balance between improved typing efficiency and ease of transition from the Qwerty layout.
Impact On Hand And Finger Movements
The layout of a keyboard can significantly impact the movements of your hands and fingers while typing. Let’s explore how Qwerty, Dvorak, and Colemak affect hand and finger movements:
- Qwerty: Qwerty’s layout often requires fingers to stretch and twist, leading to potential strain and increased risk of repetitive strain injuries (RSIs). Due to the placement of commonly used keys, some fingers may overwork while others remain underutilized.
- Dvorak: Dvorak’s layout places the most frequently used keys on the home row, minimizing the need for finger stretching and reducing strain on fingers and hands. It encourages more balanced and natural hand movements.
- Colemak: Colemak focuses on minimizing finger movement and strain. It maintains similarities with Qwerty to ease the transition, while optimizing key placement to reduce strain and maximize typing efficiency.
By considering the impact on hand and finger movements, you can choose a keyboard layout that prioritizes comfort and reduces the risk of developing RSIs. Understanding the typing efficiency and the impact on hand and finger movements offered by each layout can help you make an informed decision based on your specific needs and preferences.
Credit: m.youtube.com
Adoption And Popularity
Understanding the adoption and popularity of different keyboard layouts provides valuable insights into their usability, effectiveness, and relevance in various contexts. Here’s more on how adoption and popularity influence the use of keyboard layouts:
- Usage in Work Environments: Keyboard layouts are often tailored to suit the specific needs and preferences of users in different work environments. For example, traditional QWERTY layouts are widely used in office settings and industries where familiarity and compatibility with standard keyboards are prioritized. However, alternative layouts such as Dvorak, Colemak, and ergonomic designs like split-key and contoured keyboards are gaining traction among users seeking improved comfort, efficiency, and ergonomics. In specialized fields such as programming, data entry, and transcription, users may adopt alternative layouts to optimize typing speed, reduce fatigue, and minimize the risk of repetitive strain injuries.
- Community Preferences and Trends: Community feedback and trends play a significant role in shaping the adoption of alternative keyboard layouts. Online communities, forums, and social media platforms provide platforms for users to share their experiences, discuss keyboard preferences, and advocate for alternative layouts. The popularity of layouts like Dvorak and Colemak, for example, has grown over the years due to the advocacy and support of enthusiasts and ergonomic experts. Additionally, advancements in keyboard technology and the availability of customizable layouts have contributed to the diversification of keyboard preferences and the exploration of innovative designs.
- Ergonomic Considerations: The adoption of alternative keyboard layouts is often driven by ergonomic considerations and the desire to minimize discomfort and strain during typing. Ergonomic keyboards, such as split-key and contoured designs, are designed to promote a more natural hand position and reduce stress on the wrists, arms, and shoulders. As awareness of ergonomic principles and the importance of workplace health and safety grows, more users are seeking out ergonomic keyboard solutions to enhance comfort and productivity.
- Accessibility and Learning Curve: Despite the potential benefits of alternative keyboard layouts, adoption may be limited by factors such as accessibility and the learning curve associated with mastering new layouts. Users accustomed to traditional QWERTY layouts may be hesitant to switch to alternative layouts due to concerns about compatibility, relearning typing skills, and adapting to new key placements. However, with patience, practice, and the availability of resources such as typing tutorials and software tools, users can successfully transition to alternative layouts and reap the benefits of improved comfort and efficiency.
By considering factors such as usage in work environments, community preferences, ergonomic considerations, and accessibility, users can make informed decisions when exploring alternative keyboard layouts and choosing the most suitable option for their needs and preferences.
Transitioning Between Layouts
Transitioning between different keyboard layouts like Qwerty, Dvorak, and Colemak can be a challenging yet rewarding process. Understanding the challenges and benefits of such a transition is essential to effectively make the switch.
Challenges And Benefits
- Challenges: Muscle memory re-learning, typing speed decrease.
- Benefits: Increased typing speed, reduced strain on fingers.
Tips For Smooth Transition
- Practice consistently.
- Use online training tools.
- Focus on specific key groups initially.
Future Trends In Keyboard Layouts
As technology advances, the future of keyboard layouts is set to become more diverse and innovative. With the increasing demand for personalized and customizable experiences, users are looking for keyboards that cater to their specific needs and preferences. In this section, we will explore two key future trends in keyboard layouts: customization and personalization, as well as innovations and emerging designs.
Customization And Personalization
One of the significant future trends in keyboard layouts is the ability to customize and personalize the layout according to individual preferences. With the development of advanced software and firmware, users can now create their own unique keyboard layouts. This level of customization offers a myriad of benefits, allowing users to optimize their typing experience and enhance productivity.
Some key customization options include remapping keys, adjusting key sensitivity, and changing the layout to suit specific needs. For instance, programmers may prefer to have frequently used programming keys easily accessible, while gamers may want a layout that prioritizes gaming commands. By customizing and personalizing their keyboard layouts, users can create a setup that aligns perfectly with their workflow and enhances their overall user experience.
Innovations And Emerging Designs
With the increased demand for ergonomic keyboards and the desire to reduce typing-related injuries, manufacturers are constantly exploring and developing innovative keyboard designs. These designs aim to improve comfort, reduce strain, and allow for more efficient typing.
One such emerging design is the split keyboard layout, which divides the keyboard into two separate halves, with each half catering to one hand. This design promotes a more natural hand positioning and reduces the risk of repetitive stress injuries.
Another innovation is the introduction of alternative keyboard layouts, such as the Dvorak and Colemak layouts. These layouts are designed to optimize typing efficiency by placing commonly used keys in more accessible positions. While the QWERTY layout is the most widely used, the emergence of alternative layouts highlights the ongoing quest for improved typing speed and accuracy.
Frequently Asked Questions On Understanding Keyboard Layouts: Qwerty Vs. Dvorak Vs. Colemak
Is Colemak Really Better Than Qwerty?
Yes, Colemak is designed for faster, more comfortable typing than QWERTY. It reduces finger movement and strain.
Should I Switch To Colemak Or Dvorak?
Switching to Colemak or Dvorak can improve typing efficiency and reduce strain. Choosing between them depends on personal preference and commitment to learning a new layout. Consider trying both and opting for the one that feels more comfortable and productive.
What Are The 4 Keyboard Layouts?
The 4 keyboard layouts are QWERTY, AZERTY, QWERTZ, and Dvorak. Each layout has a unique arrangement of keys.
What Are The Three 3 Types Of Keyboard?
The three types of keyboards are membrane, mechanical, and chiclet, each offering unique typing experiences.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between Qwerty, Dvorak, and Colemak keyboard layouts is essential for optimizing typing efficiency and comfort. Each layout has its advantages and drawbacks, but ultimately the choice depends on individual preferences and typing needs. Whether you stick with the popular Qwerty or explore the alternative layouts, exploring and adapting to different keyboard layouts can enhance your typing experience.
So, find the layout that suits you best and start typing away with comfort and ease.